Interpret tables
Key notes !
1. Understanding Tables
- Tables organize data into rows and columns to present information clearly.
- Each row typically represents a category or group, and each column represents a variable or attribute.

2. Components of a Table
- Title: Describes the purpose or content of the table.
- Rows: List the different categories or items being measured.
- Columns: Show the variables or measurements related to each category.
- Frequency: Indicates how often a particular value or event occurs.
3. Steps to Interpret a Table
- Identify the Title: Understand the context of the data presented.
- Read the Column Headings: Determine what each column represents (e.g., frequency, number of items).
- Examine the Data: Look at the values in the table to identify patterns or key information.
- Answer Specific Questions: Use the data to respond to questions, such as finding the highest or lowest value or calculating totals.
4. Practical Application Examples
- Frequency Tables: Used to show how often different events or values occur. For example, in a game show, how often a wheel stops on a particular number.

- Problem-Solving: Tables can help answer questions like “Which number was spun the most?” or “How many students made more than a certain number of items?”
5. Interpreting Frequency Tables
- Highest Frequency: Identify the row with the highest frequency to determine the most common event or value.
- Cumulative Frequency: Add frequencies across several rows to answer questions about cumulative occurrences .
Learn with an example
🗼 A fashion magazine poll asks how many winter hats each reader owns.
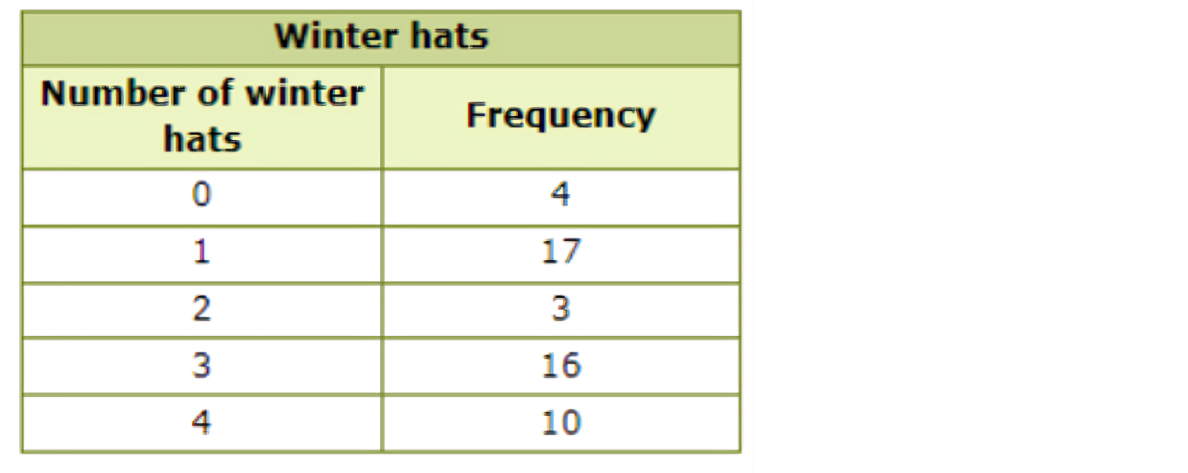
How many readers have exactly 3 winter hats?
Find the row for 3 hats and read the frequency. The frequency is 16.
16 readers have exactly 3 winter hats.
🗼While working as a summer camp counsellor, Vijay monitored how many candy necklaces each child made.
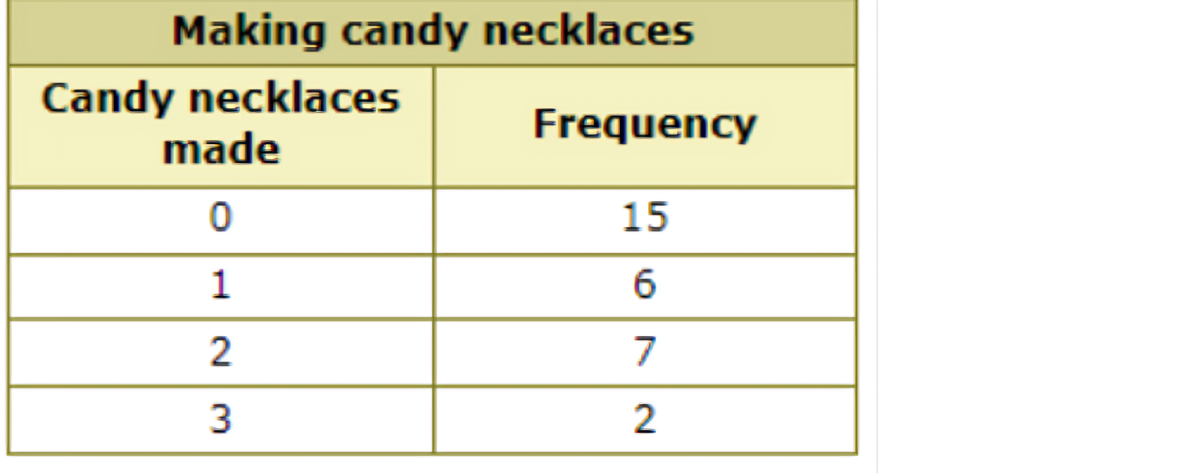
How many children made at least 1 candy necklace?
Find the rows for 1, 2, and 3 candy necklaces. Add the frequencies for these rows.
Add:
6 + 7 + 2 = 15
15 children made at least 1 candy necklace.
🗼 A marketing research firm asked people how many times they visited the mall last month.
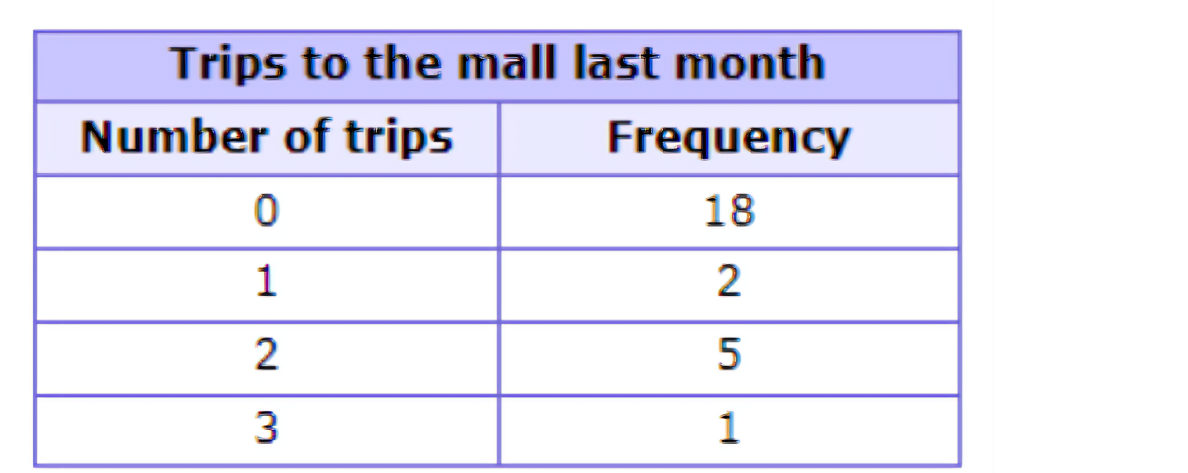
How many people are there in all?
Add the frequencies for each row.
Add:
18 + 2 + 5 + 1 = 26
There are 26 people in all.
let’s practice!

