Model and solve equations using algebra tiles
Class:8 Topic: Model and solve equations using algebra tiles by Delta publications
| What Are Algebra Tiles? |
Algebra tiles are colored shapes that represent numbers and variables:
- Small yellow squares → represent +1 (unit tile)
- Small red squares → represent -1 (negative unit tile)
- Large green rectangles → represent +x (variable tile)
- Large red rectangles → represent -x (negative variable tile)
- Large blue squares → represent x² (used in advanced problems)
| Purpose of Algebra Tiles |
- To visualize equations and expressions
- To model solving steps without guessing
- To understand balancing in equations
| Steps to Solve Equations with Algebra Tiles |
Step 1: Represent the equation
Example: x + 3 = 5
- Use 1 green rectangle (x)
- Use 3 yellow squares (+3) on the left
- Use 5 yellow squares (+5) on the right
Step 2: Keep the balance
- The two sides of the equation are like a balance scale.
- Whatever you do to one side, you must do to the other.
Step 3: Remove equal tiles from both sides
- Remove 3 yellow squares from both sides.
- Now the left side has only x, and the right side has 2 yellow squares.
Step 4: Find the value of x
- The green rectangle = 2 yellow squares
- So, x = 2
| Another Example with Negatives |
Example: x – 2 = 3
Model it:
- 1 green rectangle (x)
- 2 red squares (-1 each) on the left
- 3 yellow squares on the right
Remove the -2 from the left by adding 2 yellow squares to both sides.
Left: x
Right: 3 yellow + 2 yellow = 5 yellow squares
- Answer: x = 5
| Key Rules |
- Always keep the equation balanced.
- Remove or add tiles on both sides equally.
- Positive tiles and negative tiles cancel each other:
- (+1) + (-1) = 0
- (+x) + (-x) = 0
| Practice Problems |
Use algebra tiles to solve:
- x + 4 = 7
- x – 3 = 2
- x + 2 = –1
- –x + 3 = 1
- 2x + 1 = 5
Learn with an example
Which equation does this set of algebra tiles represent?
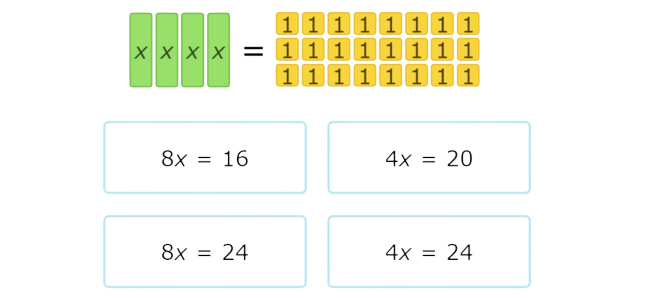
Look at the tiles on the left side of the set.

Which equation does this set of algebra tiles represent?
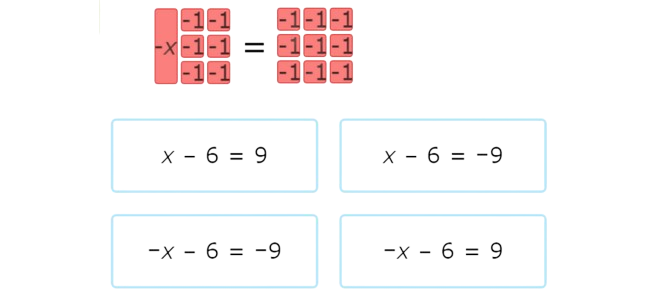
Look at the tiles on the left side of the set.

Which equation does this set of algebra tiles represent?
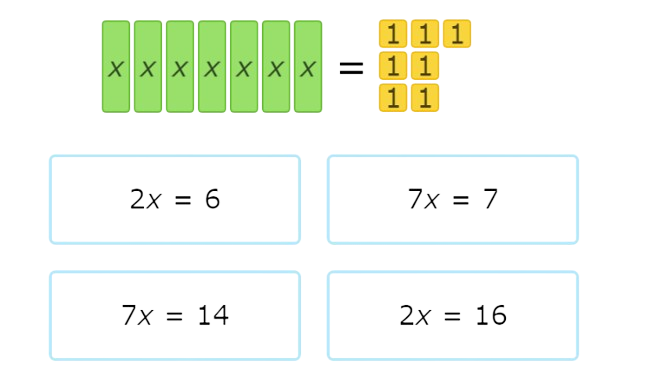
Look at the tiles on the left side of the set.

let’s practice!

