Comparison Of Plant And Animal Cells
comparison of plant and animal cell by Delta publications
key notes:
Overview
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic cells, but they have some key similarities and differences.
Similarities
Both plant and animal cells share the following structures:
Cell Membrane: Controls the entry and exit of substances.
Cytoplasm: Jelly-like substance where cellular activities occur.
Nucleus: Contains genetic material (DNA) and controls cellular activities.
Mitochondria: Powerhouse of the cell, produces energy.
Ribosomes: Synthesize proteins.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):
- Rough ER: Has ribosomes and helps in protein synthesis.
- Smooth ER: Helps in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins.
Lysosomes: Contain enzymes to digest waste (more prominent in animal cells).
Unique Features of Plant Cells
- Cell Wall: Provides structure and support, made of cellulose.
- Chloroplasts: Contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
- Large Central Vacuole: Stores water, nutrients, and waste, maintains turgor pressure.
Unique Features of Animal Cells
- Cilia and Flagella: Some animal cells have these for movement.
- Centrioles: Help in cell division.
- Small Vacuoles: Present but smaller and more numerous.
Comparison Table
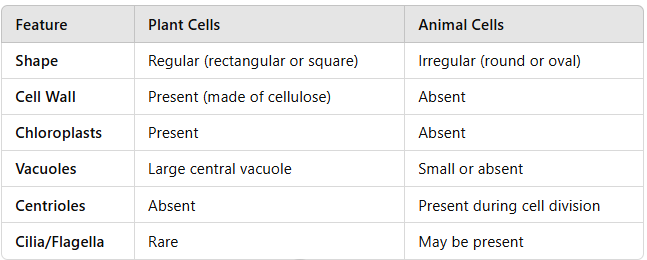
Function-Based Differences
- Plant Cells: Specialized for photosynthesis and structural support.
- Animal Cells: Specialized for mobility and complex interactions with the environment.
Let’s practice!

