Cell Structure And Function
key notes:
Introduction to Cells:
- Definition: Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms.
- All living things are made up of cells, and they perform essential functions to sustain life.
Types of Cells:
- Prokaryotic Cells: Simple cells without a nucleus (e.g., bacteria).
- Eukaryotic Cells: More complex cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (e.g., plant and animal cells).
Parts of the Cell:
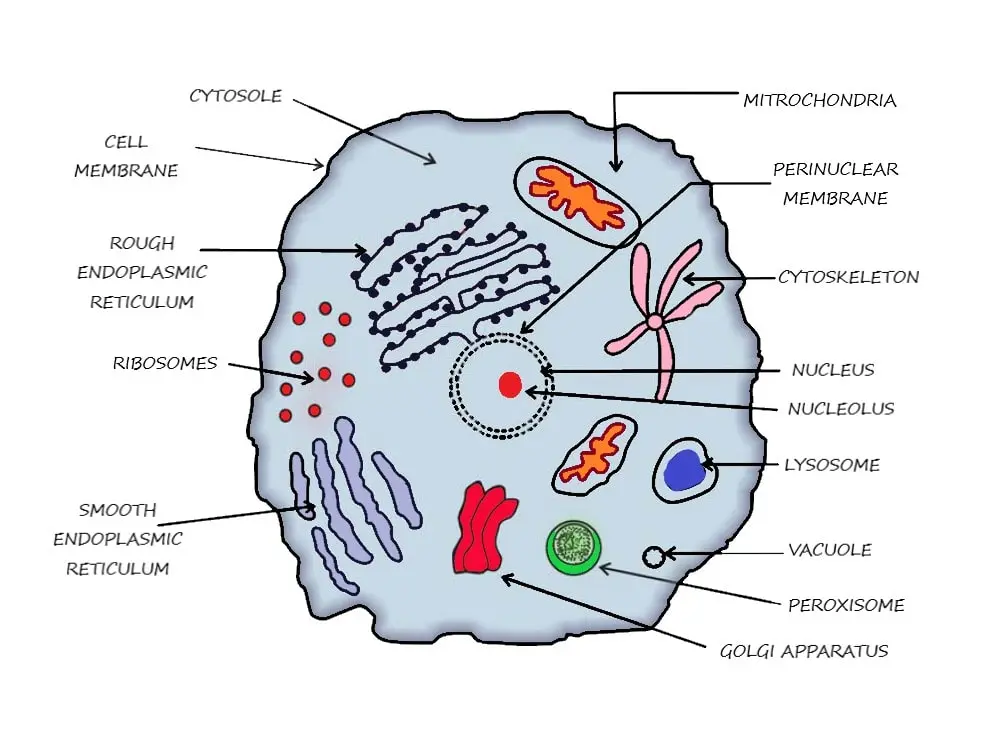
Cell Membrane: Protects and supports the cell, regulates what enters and leaves the cell (selectively permeable).
Nucleus: The control center of the cell; contains genetic material (DNA).
Cytoplasm: Gel-like substance where cell activities occur and where organelles are located.
Mitochondria: The powerhouse of the cell; produces energy (ATP) through cellular respiration.
Ribosomes: Small structures where protein synthesis occurs.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):
- Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes; involved in protein synthesis.
- Smooth ER: No ribosomes; involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
Golgi Apparatus: Packages and transports proteins and lipids within or outside the cell.
Lysosomes: Contain digestive enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris.
Vacuoles: Storage organelles; store nutrients, waste products, or help in maintaining turgor pressure in plant cells.
Chloroplasts (in plant cells): Contain chlorophyll and conduct photosynthesis, converting sunlight into food energy.
Cell Wall (in plant cells): Provides structural support and protection, made of cellulose.
Cell Function:
- Energy Production: Mitochondria break down glucose to produce energy (ATP) for cell functions.
- Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes create proteins by reading RNA instructions.
- Transport: The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus help transport proteins and lipids.
- Waste Removal: Lysosomes break down waste and foreign material.
- Reproduction: Cells reproduce through processes like mitosis (for growth) and meiosis (for sexual reproduction).
Difference Between Plant and Animal Cells:
- Plant Cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and a large central vacuole.
- Animal Cells lack a cell wall, chloroplasts, and have smaller vacuoles.
Cell Division:
- Mitosis: Process by which eukaryotic cells divide to produce two genetically identical daughter cells for growth or repair.
- Meiosis: Cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating gametes (sperm and eggs) for reproduction.
Importance of Cells:
- Understanding cell structure and function helps in studying diseases, medicine, and biotechnology.
- Cells are essential for life; they perform all vital functions, including energy production, reproduction, and responding to the environment.
Let’s practice!

