Biotic COMPONENTS
Key Notes:
1. What Are Biotic Components?
- Biotic components refer to all living organisms in an ecosystem.
- These include plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms.
2. Interdependence:
- Biotic components are interconnected and depend on each other for survival.
- For example, plants need animals for pollination, and animals depend on plants for food.
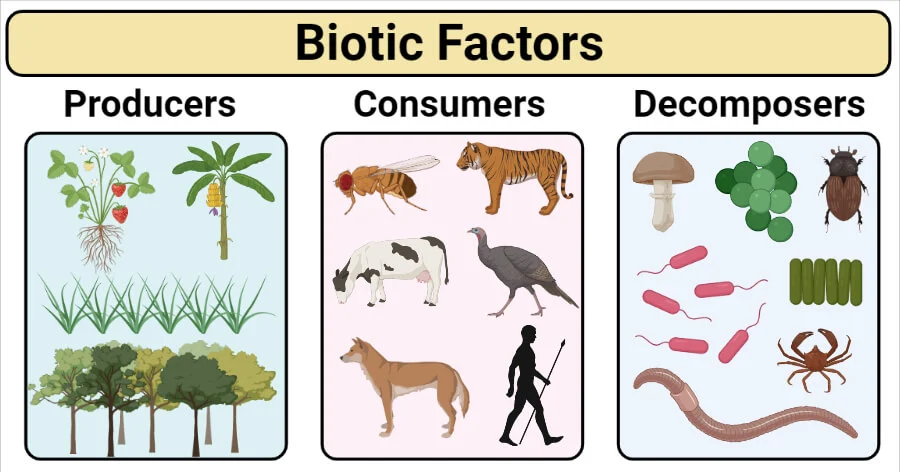
3. Producers, Consumers, Decomposers:
- Biotic components can be categorized into three groups:
- Producers: Organisms like plants that produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- Consumers: Organisms that eat other organisms for energy. They can be herbivores (plant-eaters), carnivores (meat-eaters), or omnivores (both plant and meat-eaters).
- Decomposers: Organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organic matter into nutrients that can be used by other organisms.
4. Food Chains and Food Webs:
- Biotic components are connected through food chains and food webs.
- Food chains show the flow of energy from one organism to another. For example, grass -> rabbit -> fox.
- Food webs are more complex and show multiple interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.
5. Adaptations:
- Biotic components have specific traits and adaptations that help them survive in their environment.
- For example, animals may have camouflage or specialized body parts for hunting or defense.
6. Competition and Niches:
- Biotic components often compete for resources like food, water, and shelter.
- Each species occupies a specific ecological niche, which is its role in the ecosystem.
7. Human Impact:
- Human activities can have a significant impact on biotic components through habitat destruction, pollution, over-hunting, and more.
- Conservation efforts aim to protect and preserve biotic components and their habitats.
8. Importance of Biodiversity:
- Biotic components contribute to the biodiversity of an ecosystem.
- High biodiversity is essential for the health and stability of ecosystems.
9. Examples of Biotic Components:
- Plants: Trees, grasses, flowers
- Animals: Birds, mammals, reptiles, insects
- Microorganisms: Bacteria, fungi, algae
10. Balance in Ecosystems: – Maintaining a balance among biotic components is crucial for the overall health of an ecosystem. – Changes in one population can have ripple effects throughout the ecosystem.
Let’s practice!

