Nitrogen Cycle
nitrogen cycle by Delta publications
key notes:–
🌱 Nitrogen Cycle – Key Notes
🔹 What is Nitrogen?
- Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless gas.
- It makes up about 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Plants and animals need nitrogen to build proteins and grow.
🔄 What is the Nitrogen Cycle?
- The Nitrogen Cycle is the process by which nitrogen moves between the air, soil, plants, animals, and back into the air.
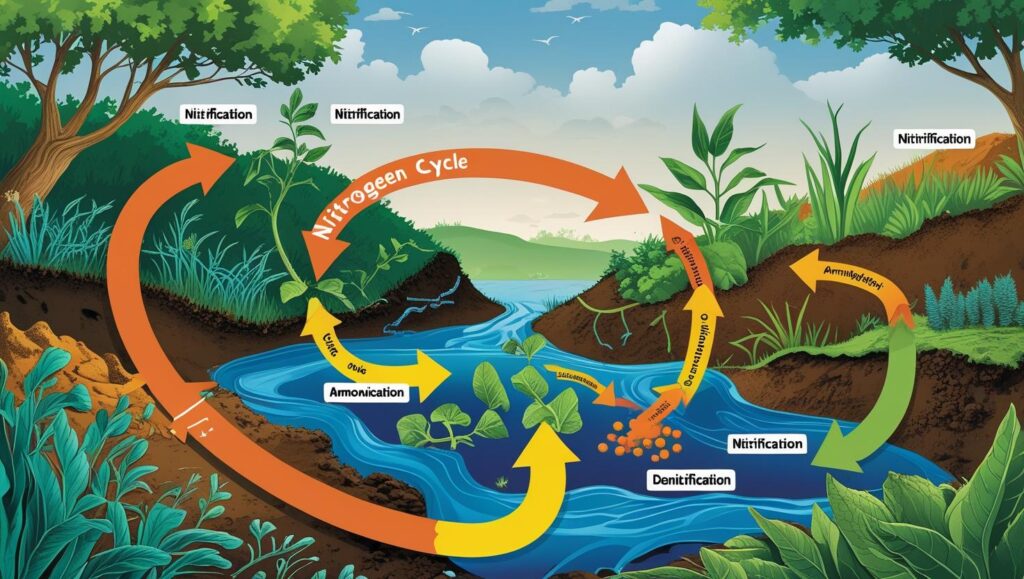
🔍 Steps in the Nitrogen Cycle:
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen in the air (N₂) is converted into a usable form (like ammonia).
Done by:
- Lightning (natural)
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria (in soil or root nodules of plants like peas, beans).
Nitrification
- Ammonia is changed into nitrates and nitrites by bacteria in the soil.
- These are forms plants can absorb.
Assimilation
- Plants absorb nitrates from the soil.
- Animals eat plants and use nitrogen to build proteins.
Ammonification (Decay)
- When plants and animals die, decomposers (like bacteria and fungi) break them down.
- Nitrogen returns to the soil as ammonia.
Denitrification
- Other bacteria convert nitrates back into nitrogen gas (N₂).
- This gas returns to the atmosphere, completing the cycle.
🌾 Importance of the Nitrogen Cycle
- Helps in plant growth.
- Maintains balance of nitrogen in the atmosphere.
- Supports food chains and ecosystems.
🧠 Fun Fact:
- Without the nitrogen cycle, plants wouldn’t grow, and all life on Earth would be affected!
let’s practice!

