Nitrogen Fixation
nitrogen fixation by Delta publications
key notes :-
What is Nitrogen Fixation?
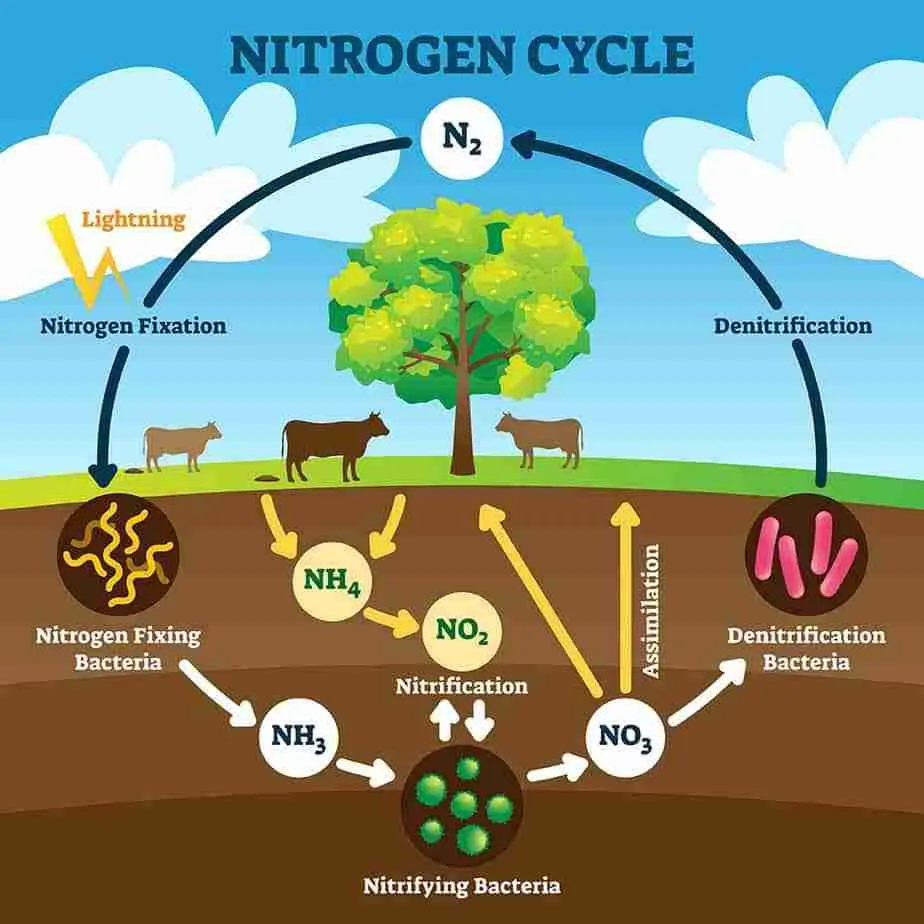
- Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N₂), which cannot be directly used by most living organisms, into a form like ammonia (NH₃) or other compounds that plants can absorb and use.
Importance of Nitrogen
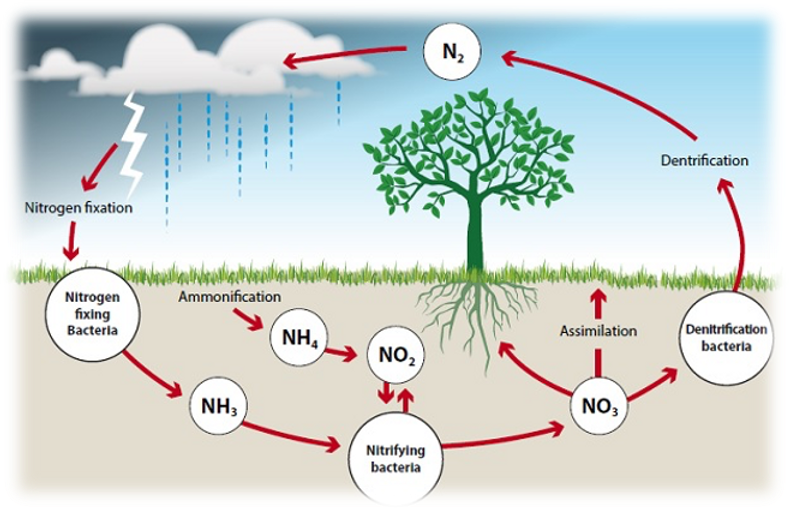
- Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plants as it is a critical component of amino acids, proteins, DNA, and chlorophyll. It helps in plant growth, development, and reproduction.
Atmospheric Nitrogen
- The atmosphere consists of about 78% nitrogen gas. However, plants and animals cannot use nitrogen in its gaseous form directly.
Types of Nitrogen Fixation
- Biological Nitrogen Fixation: Carried out by certain bacteria and cyanobacteria (blue-green algae).
- Industrial Nitrogen Fixation: Through the Haber-Bosch process, nitrogen is converted into fertilizers.
- Natural Nitrogen Fixation: Occurs due to lightning which converts nitrogen gas into nitrates.
Role of Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria
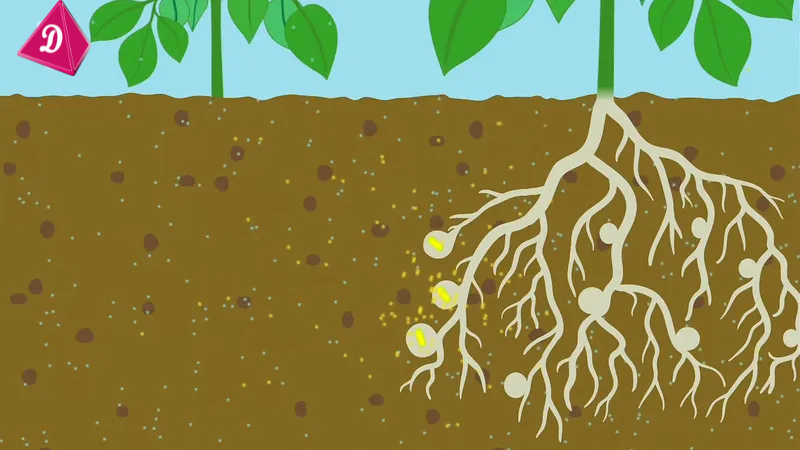

- Certain bacteria like Rhizobium, which live in the root nodules of leguminous plants (e.g., peas, beans), convert atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms.
- Free-living bacteria like Azotobacter and Clostridium also contribute to nitrogen fixation in the soil.
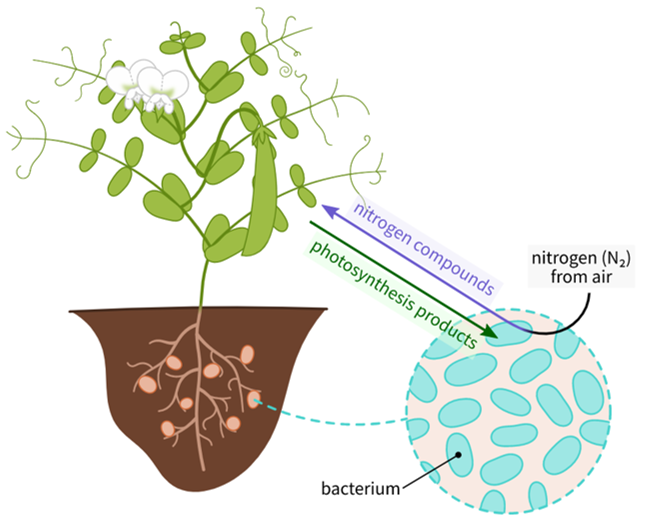
Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation
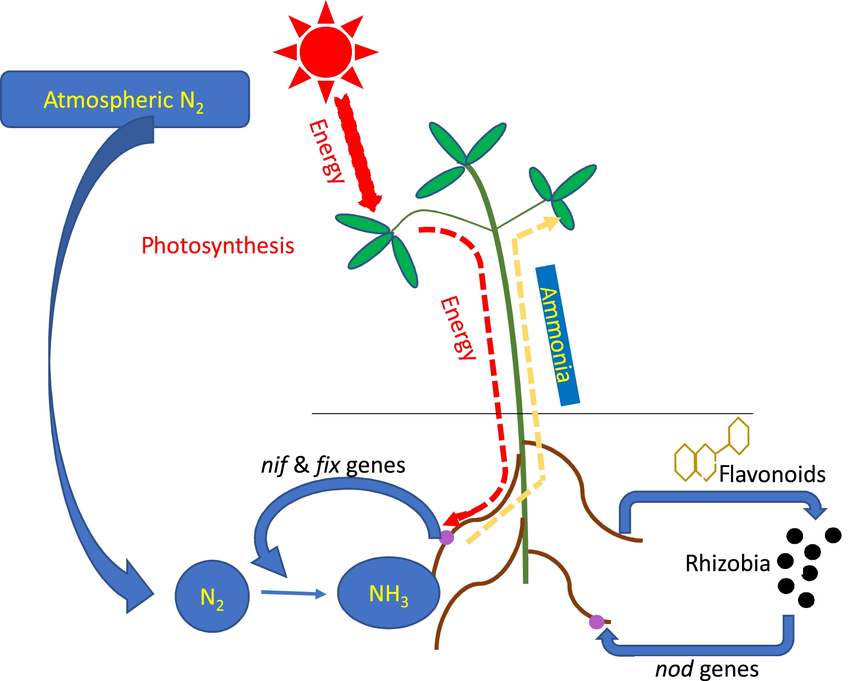
- In a symbiotic relationship, bacteria like Rhizobium live in root nodules of leguminous plants and provide them with nitrogen compounds while receiving carbohydrates and shelter from the plant.
Non-Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation
- Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia independently, without forming relationships with plants.
Nitrogen Fixation by Lightning
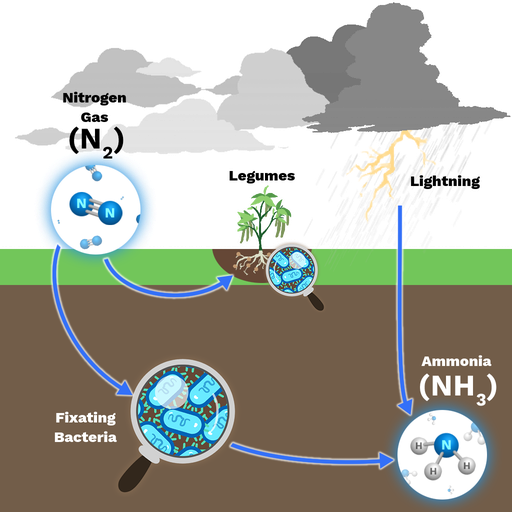
- During thunderstorms, the high energy from lightning converts atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen oxides, which dissolve in rainwater and form nitrates that plants can absorb.
Significance of Nitrogen Fixation
- Nitrogen fixation enriches the soil with nutrients, helping plants grow healthier. This process is crucial in agriculture to ensure better crop yields.
Human Impact
- Excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers can lead to environmental issues like water pollution (eutrophication) and soil degradation.
Let’s practice!

