Food Preservation
preservatives by Delta publications
key notes :
✅ What is Food Preservation?
Food preservation is the process of treating and handling food to prevent spoilage, decay, or contamination, and to extend its shelf life.
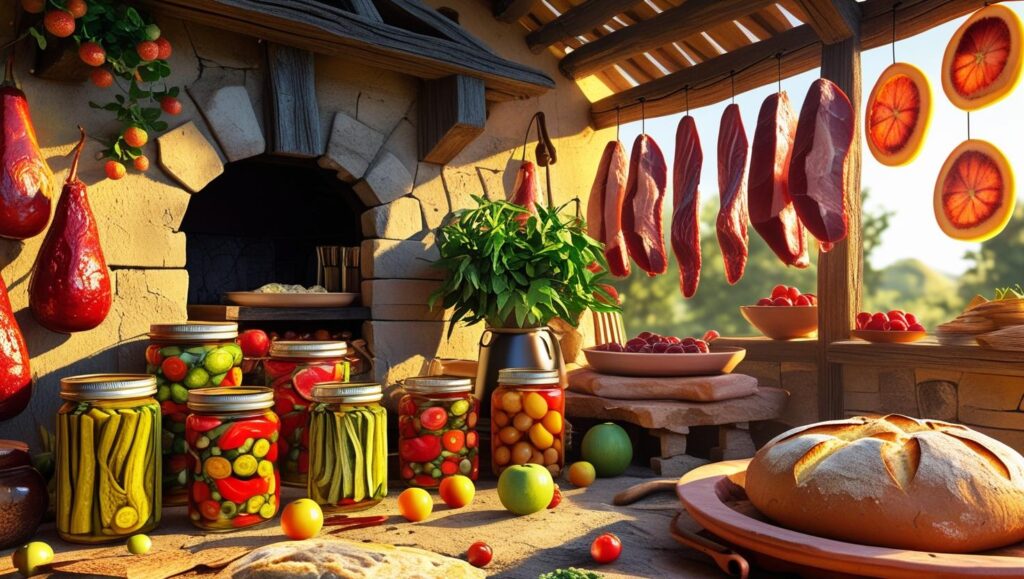

🧫 Why Do We Preserve Food?
- To prevent the growth of microorganisms (like bacteria and fungi).
- To avoid wastage of food.
- To store food for longer periods.
- To ensure food is available during off-seasons.
🧃 Common Methods of Food Preservation
| Method | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | Removes moisture to stop bacteria growth | Dried fruits, grains |
| Refrigeration | Slows down the activity of bacteria | Milk, vegetables |
| Freezing | Stops microbial growth completely | Ice cream, frozen peas |
| Canning | Sealing food in airtight containers after heating | Jam, beans |
| Salting | Removes water and kills microbes | Pickles, fish |
| Sugaring | High sugar content prevents microbial growth | Jams, jellies |
| Pasteurization | Heating food to kill harmful microbes | Milk, juices |
| Vacuum Packing | Removes air to slow spoilage | Chips, processed meat |
| Chemical Preservation | Using preservatives to stop microbial growth | Soft drinks, ketchup |
🦠 Common Preservatives Used
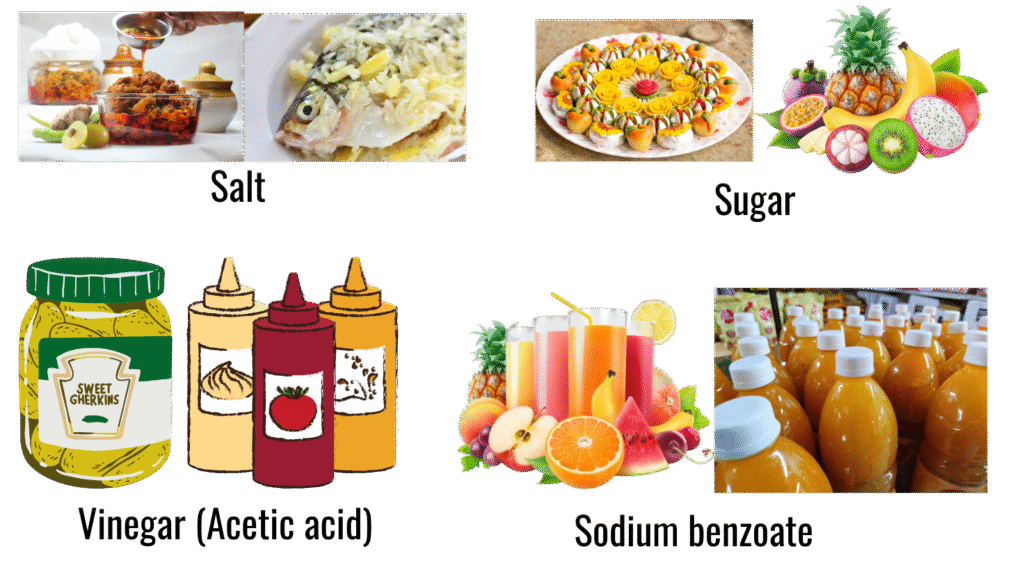
- Salt – for fish, pickles
- Sugar – for fruits, sweets
- Vinegar (Acetic acid) – for pickles, sauces
- Sodium benzoate – for juices, soft drinks
🧪 Natural vs Artificial Preservatives
- Natural: Salt, sugar, vinegar, lemon juice
- Artificial: Sodium benzoate, potassium metabisulfite
⚠️ Precautions in Food Preservation
- Use clean containers and hands.
- Store preserved food in cool, dry places.
- Check expiry dates if preservatives are used.
🧠 Quick Facts
- Louis Pasteur developed pasteurization.
- Preservation helps in food security.
- Overuse of artificial preservatives can be harmful.
Let’s practice!

