Harmful Microorganisms
harmful micro organisms by Delta publications
key notes :
🔹 What Are Harmful Microorganisms?
- Microorganisms that cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants or spoil food and materials are called harmful microorganisms.
- These are also known as pathogens (when they cause disease).
🔹 Types of Harmful Microorganisms
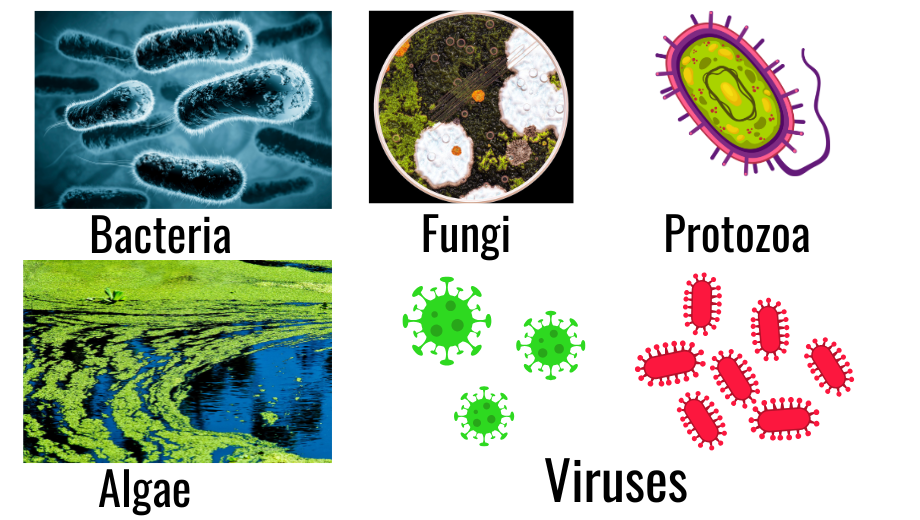
- Bacteria
- Cause diseases like cholera, typhoid, tuberculosis.
- Some bacteria also spoil food.
- Viruses
- Cause diseases like common cold, influenza, COVID-19, AIDS.
- They can infect humans, animals, and plants.
- Fungi
- Cause skin infections like athlete’s foot.
- Spoil food like bread and fruits by growing molds.
- Protozoa
- Cause diseases like malaria and amoebic dysentery.
🔹 Diseases Caused by Harmful Microorganisms
| Disease | Type of Microorganism | Spreads Through |
|---|---|---|
| Typhoid | Bacteria | Contaminated food/water |
| Tuberculosis (TB) | Bacteria | Air (cough/sneeze) |
| Malaria | Protozoa | Mosquito bite |
| Dengue | Virus | Mosquito bite |
| COVID-19 | Virus | Air & contact |
🔹 How Harmful Microorganisms Spread
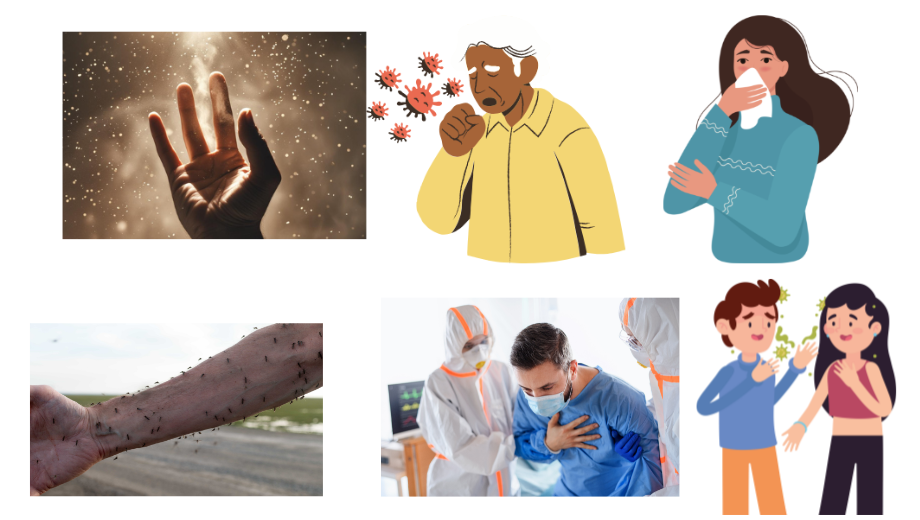

- Contaminated food and water
- Air (sneezing, coughing)
- Insects like mosquitoes (called vectors)
- Direct contact with infected person
- Touching infected surfaces
🔹 Harm to Food and Materials
- Microorganisms spoil food, making it unsafe to eat.
- Cause decay in materials like wood and cloth.
- Lead to economic losses in agriculture and storage.
🔹 Prevention and Control
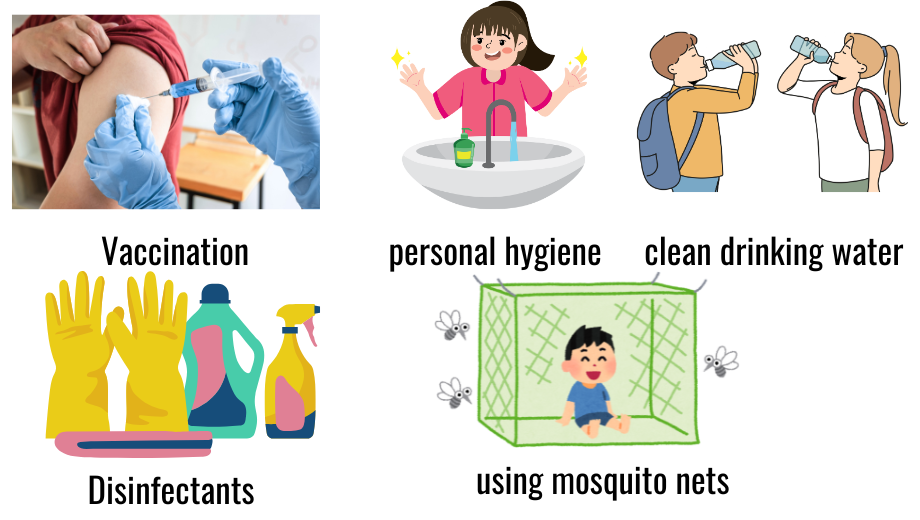
- Vaccination (e.g., polio, measles)
- Maintain personal hygiene
- Use clean drinking water
- Proper food storage
- Disinfectants to kill germs
- Controlling vectors (e.g., using mosquito nets)
Let’s practice!

