Micro-Organisms
micro organisms by Delta publications
key notes :-
What are Micro-Organisms?
- Micro-organisms, also known as microbes, are tiny living organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. They can only be observed using a microscope.
- Examples include bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae.
Types of Micro-Organisms
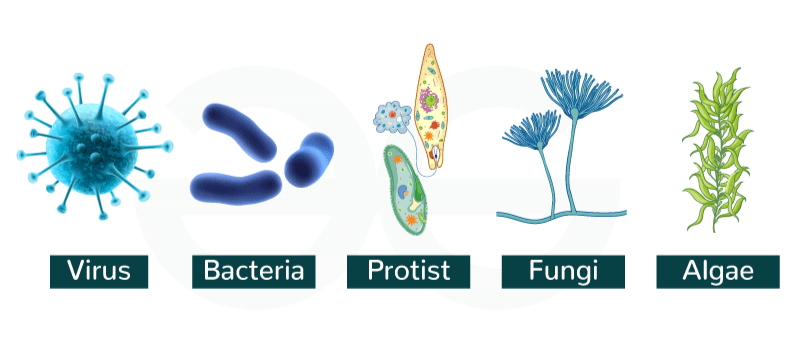
- Bacteria: Single-celled organisms found in various environments. Some are beneficial (e.g., in digestion), while others can cause diseases (e.g., tuberculosis).
- Viruses: Non-living outside a host but can reproduce within living cells, causing diseases like the flu, chickenpox, and COVID-19.
- Fungi: Can be unicellular (like yeast) or multicellular (like molds and mushrooms). Some fungi are used in food production (e.g., bread making), while others can cause infections.
- Protozoa: Single-celled organisms found in water and soil; some are harmful, such as those causing malaria.
- Algae: Simple, plant-like organisms found in water that produce oxygen through photosynthesis.
Where Do Micro-Organisms Live?
- Micro-organisms are found almost everywhere—in soil, water, air, and even inside the bodies of other organisms.
- They can thrive in extreme conditions, such as hot springs, deep oceans, and polar ice caps.
Useful Micro-Organisms
- In Food Production:
- Bacteria are used in making curd, cheese, and vinegar.
- Yeast is used in baking and brewing to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide.
- In Medicine:
- Antibiotics, such as penicillin, are produced by certain fungi and bacteria to treat bacterial infections.
- In Agriculture:
- Certain bacteria (like Rhizobium) help fix nitrogen in the soil, enriching its fertility.
- In Decomposition:
- Micro-organisms break down organic waste, turning it into compost, which improves soil quality.
Harmful Micro-Organisms

- Pathogens are micro-organisms that cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants.
- Diseases caused by bacteria: Tuberculosis, cholera.
- Diseases caused by viruses: Influenza, measles, AIDS.
- Fungal infections: Athlete’s foot, ringworm.
- Protozoan diseases: Malaria, amoebic dysentery.
Role of Micro-Organisms in Environmental Balance
- Micro-organisms play a crucial role in decomposition, recycling nutrients back into the environment.
- They are essential in processes like nitrogen fixation, which is vital for plant growth.
Prevention of Microbial Diseases
- Vaccinations help protect against viral and bacterial infections.
- Good hygiene practices such as washing hands, properly cooking food, and drinking clean water can reduce the spread of harmful microbes.
- Using disinfectants and antibiotics helps control microbial growth.
Biotechnology and Micro-Organisms
- Micro-organisms are used in genetic engineering to produce insulin, vaccines, and other bio-products.
- They play a significant role in industries like waste management and biofuel production.
Let’s practice!

