Electroplating
key notes :
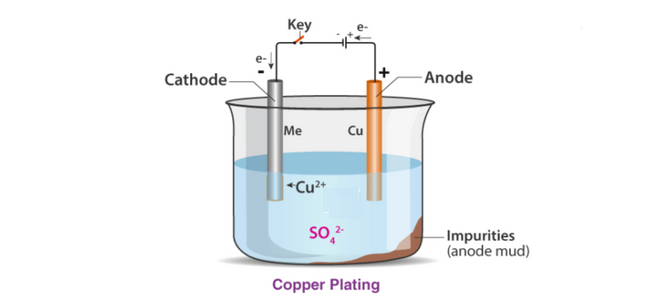
What is Electroplating?
- Electroplating is a process in which a metal coating is applied to an object’s surface by using electrical current. It is commonly used to improve the appearance and durability of various items.
How does Electroplating Work?
- Electroplating involves two key components: an anode (positive electrode) and a cathode (negative electrode), both immersed in an electrolyte solution.
- The object to be plated is connected to the cathode, while a metal (often the same as the coating metal) is connected to the anode.
- When electric current is applied, metal ions from the anode dissolve in the electrolyte and are deposited onto the cathode (the object) as a thin, even layer.
- Purpose of Electroplating:
- Improve Appearance: Electroplating can enhance the appearance of objects by giving them a shiny, metallic finish.
- Prevent Corrosion: It provides a protective layer that prevents the underlying material from corroding.
- Increase Durability: Electroplating can make objects more resistant to wear and tear.
- Create Decorative Finishes: It’s used for decorative purposes, such as creating gold or silver finishes on jewelry.
- Common Metals Used in Electroplating:
- Chromium: Used for chrome plating on automotive parts and kitchen appliances.
- Nickel: Often used as an undercoat before applying another metal, like chrome or gold.
- Gold and Silver: Used for jewelry and decorative items.
- Copper: Used for electrical connectors and as a base layer for other metals.
- Applications of Electroplating:
- Jewelry making: Gold and silver electroplating for jewelry pieces.
- Automotive industry: Chrome plating for car bumpers and trim.
- Electronics: Copper plating on printed circuit boards.
- Household items: Nickel plating on faucets and kitchenware.
- Aerospace: Electroplating is used to protect aircraft components from corrosion.
- Environmental Concerns:
- Electroplating can produce waste and potentially harmful chemicals, so proper disposal and waste management are crucial.
- Regulations and practices have been developed to minimize the environmental impact of electroplating processes.
- Safety Precautions:
- Electroplating involves the use of electricity and chemicals, so safety measures like wearing protective gear and working in well-ventilated areas are essential.
Let’s practice!

