Electrolytic Cell
key notes :
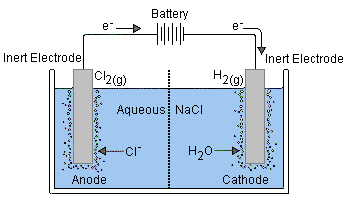
An electrolytic cell is a device used in chemistry to facilitate a process called electrolysis, where electrical energy is used to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Here are some key notes on the topic “Electrolytic Cell” suitable for grade 8 students:
- Definition: An electrolytic cell is a laboratory apparatus that uses an external electric current to induce a chemical reaction, which would not occur spontaneously under normal conditions.
- Components: Electrolytic cells consist of two electrodes, typically made of inert materials like platinum or graphite, immersed in an electrolyte solution. The electrodes are connected to an external power source (battery or power supply).
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a solution that contains ions (charged particles) which can move freely. It’s necessary for the flow of electricity through the cell.
- Electrodes: Electrodes are conductive materials where oxidation (loss of electrons) occurs at the anode, and reduction (gain of electrons) occurs at the cathode. The anode is usually positively charged, and the cathode is negatively charged.
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis is the process of using electrical energy to drive a chemical reaction. It’s used to separate compounds into their constituent elements or to produce new compounds.
- Role of the Battery: The external power source (battery or power supply) provides the energy necessary to overcome the energy barrier for the non-spontaneous reactions that occur at the electrodes.
- Redox Reactions: Electrolysis involves redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions. Reduction occurs at the cathode, where positive ions gain electrons and become neutral atoms or molecules. Oxidation takes place at the anode, where negative ions lose electrons and become neutral atoms or molecules.
- Examples of Electrolysis: Electrolytic cells are used in various practical applications, such as:
- Electroplating: Coating an object with a thin layer of metal for decoration or corrosion resistance.
- Water Electrolysis: Splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen gases for fuel production.
- Electrorefining: Purifying metals like copper or aluminum by removing impurities.
- Electrolytic production of chemicals like chlorine, sodium hydroxide, and more.
- Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis: These laws describe the quantitative relationship between the amount of substance produced or consumed during electrolysis and the amount of electrical charge passed through the cell.
- Safety: Electrolytic cells involve electricity and chemical reactions. It’s essential to follow safety precautions, such as wearing safety goggles and gloves and working in a well-ventilated area.
In summary, electrolytic cells are devices used to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions using electricity. They are essential in various industries and scientific research, and understanding their basic principles is important in chemistry.
Let’s practice!

