Greenhouse Effect
Key Notes :
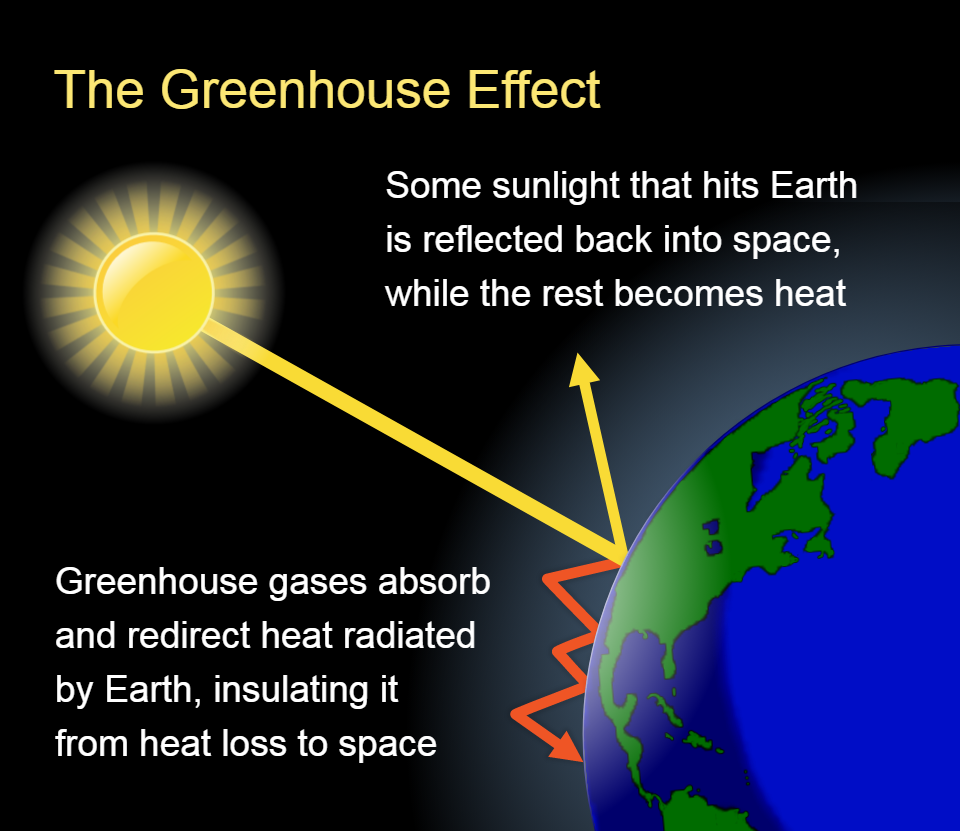
- What is the Greenhouse Effect?
- The Greenhouse Effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface.
- It’s called the “Greenhouse Effect” because it works like a greenhouse, trapping heat from the sun inside the Earth’s atmosphere.
- How Does It Work?
- Solar energy from the sun reaches the Earth’s surface as sunlight.
- Some of this energy is absorbed by the Earth and warms it.
- The Earth then emits heat energy in the form of infrared radiation.
- Greenhouse Gases:
- Certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere, known as greenhouse gases (e.g., carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor), trap some of this outgoing heat.
- They act like a blanket around the Earth, preventing too much heat from escaping into space.
- Natural vs. Enhanced Greenhouse Effect:
- The natural greenhouse effect is essential for maintaining a stable temperature on Earth, making it habitable.
- However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, enhancing the greenhouse effect.
- Consequences of Enhanced Greenhouse Effect:
- Global Warming: Increased greenhouse gases lead to a rise in average global temperatures, known as global warming.
- Climate Change: Global warming causes changes in weather patterns, leading to climate change, which can result in more extreme weather events.
- Impact on Ecosystems and Sea Levels:
- Altered temperatures and weather patterns can disrupt ecosystems, endangering plant and animal species.
- Melting ice caps and glaciers contribute to rising sea levels, which can flood coastal areas.
- Mitigation and Solutions:
- To reduce the enhanced greenhouse effect, it’s important to decrease the emission of greenhouse gases.
- This can be achieved through practices like reducing carbon emissions from cars and factories, using renewable energy sources, and conserving energy.
- International Agreements:
- Countries around the world have come together to address climate change through agreements like the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global temperature rise.
- Individual Action:
- Even individuals can help by reducing their carbon footprint, such as using energy-efficient appliances, reducing waste, and using public transportation or carpooling.
- Ongoing Research:
- Scientists continue to study the Greenhouse Effect and its consequences to better understand and address climate change.
Let’s practice!

