What Makes Things Visible
Key Notes :
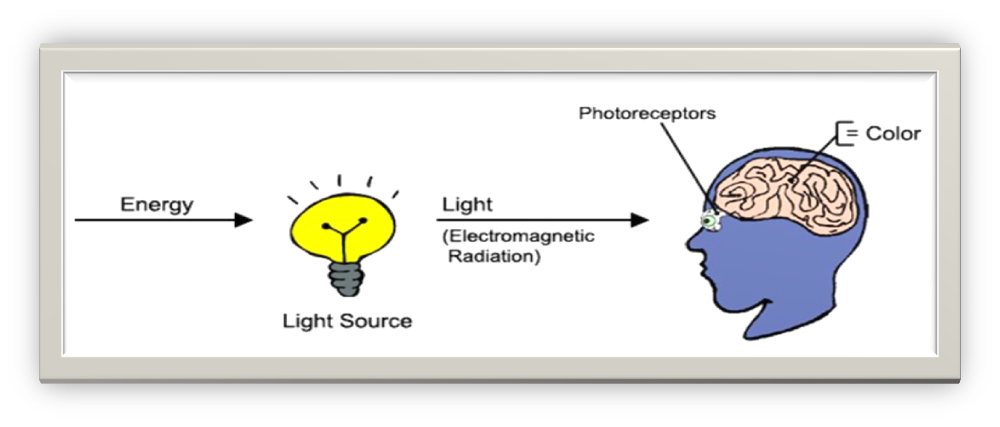
- Light as the Source of Visibility:
- Light is essential for us to see things.
- It travels in straight lines and allows us to perceive the world around us.
- Reflection of Light:
- When light falls on an object, it can either be absorbed, transmitted, or reflected.
- Reflection is when light bounces off an object’s surface.
- Opaque, Transparent, and Translucent Objects:
- Opaque objects do not allow light to pass through and cast shadows.
- Transparent objects allow light to pass through without scattering, like clear glass.
- Translucent objects allow some light to pass through but scatter it in different directions, making objects behind them less clear.
- Colors and Absorption:
- The color of an object is the result of the wavelengths of light it reflects.
- For example, a red apple appears red because it reflects red light and absorbs other colors.
- The Role of Eyes:
- Our eyes are specialized organs that capture and process light.
- The cornea and lens in our eyes focus light onto the retina, which contains light-sensitive cells called rods and cones.
- Rods and Cones:
- Rods help us see in low light conditions and detect motion.
- Cones are responsible for color vision and work best in well-lit conditions.
- Perception of Images:
- The brain processes the signals from our eyes to create the images we perceive.
- Sometimes, our brains can misinterpret what we see, leading to optical illusions.
- Shadows:
- Shadows are formed when light is blocked by an object.
- The size and shape of a shadow depend on the angle and intensity of the light source.
- Mirrors and Reflection:
- Mirrors reflect light and allow us to see ourselves and objects behind us.
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- Refraction and Lenses:
- Refraction occurs when light passes through different substances, like air to water, causing it to change direction.
- Lenses, such as convex and concave lenses, use refraction to focus or diverge light, aiding in vision correction.
- Invisibility and Camouflage:
- Some materials can bend light around them, making them appear invisible.
- Animals and military technology often use camouflage to blend into their surroundings.
- Natural vs. Artificial Light:
- Natural light comes from the sun and provides a full spectrum of colors.
- Artificial light sources, like bulbs, can vary in color temperature and affect how objects appear.
Let’s practice!

