Fluid Friction
key notes :
What is Fluid Friction?

- Fluid friction, also known as viscous friction or drag, is the force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid (a liquid or a gas).
Types of Fluid Friction:
- There are two main types of fluid friction: laminar (viscous) and turbulent friction.
Laminar Friction:
- Laminar friction occurs when a fluid flows smoothly in parallel layers with minimal mixing.
- It is characterized by a slow, steady flow and is easier to predict and control.
- The resistance to motion in laminar flow is directly proportional to the viscosity of the fluid and the size and shape of the object.
Turbulent Friction:
- Turbulent friction occurs when a fluid flows in an irregular, chaotic manner with eddies and swirls.
- It typically results in higher friction and is harder to predict and control compared to laminar flow.
Factors Affecting Fluid Friction:
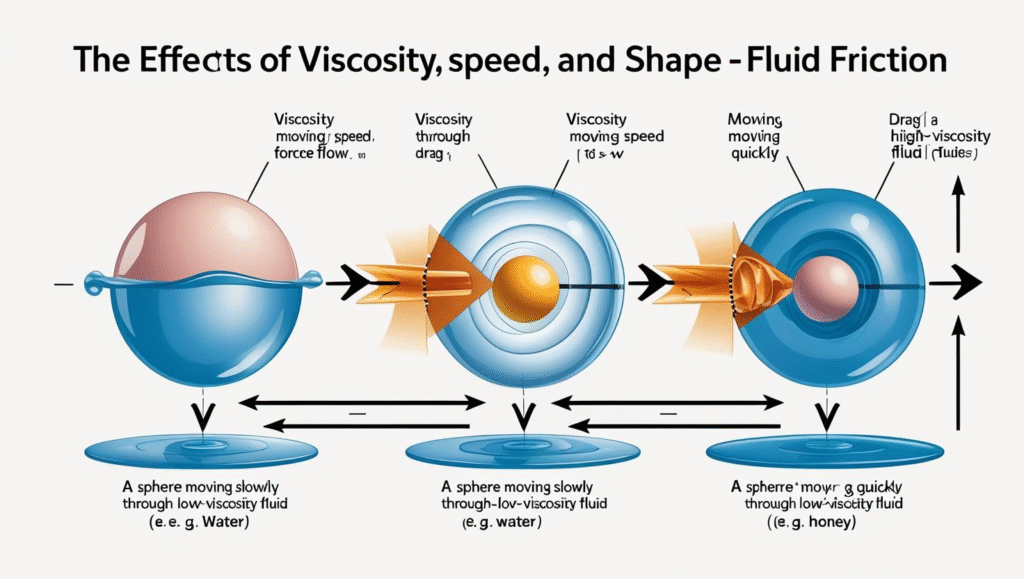
- The viscosity of the fluid: Thicker fluids (higher viscosity) have more resistance to flow.
- The speed of the object: Faster-moving objects experience greater fluid friction.
- The shape and size of the object: Objects with larger surface areas or irregular shapes encounter more fluid friction.
Applications of Fluid Friction:
- Fluid friction is encountered in various real-life situations, such as air resistance for moving vehicles and boats moving through water.
- It is essential to consider fluid friction in engineering and design to reduce energy wastage and improve efficiency.
Reducing Fluid Friction:
- To reduce fluid friction, streamline the shape of objects to minimize resistance.
- Lubricants can be used to reduce friction between moving parts in machines.
- Decreasing the speed of an object can also reduce fluid friction.
Measuring Fluid Friction:
- Scientists and engineers use instruments like viscometers to measure the viscosity of fluids.
- Experiments and simulations are conducted to study fluid friction in various scenarios.
Conclusion:
Understanding fluid friction is crucial in various fields, from engineering to transportation, as it helps in designing more efficient systems and reducing energy consumption.
Let’s practice!

