Evaluate negative exponents
Key Notes :
🌟 Evaluate Negative Exponents 🌟
| 🔹 What Are Exponents? |
An exponent shows how many times a number (called the base) is multiplied by itself.
- 👉 Example: 23=2×2×2=8
| 🔹 What Are Negative Exponents? |
A negative exponent means take the reciprocal (flip the base) and make the exponent positive.
👉 Example:
- 2−3=1/23=1/8
🧠 Rule:
a−n=1/an (where a≠0)
| 🔹 Examples |
- 5−2=1/52=1/25
- 10−1=1/101=1/10
- (2/3)−2=(3/2)2=9/4
| 🔹 Important Properties of Exponents |
1. Product of powers:
am×an=am+n
2. Quotient of powers:
am/an=am−n
3. Power of a power:
(am)n=am×n
4. Zero exponent:
a0=1 (where a≠0)
5. Negative exponent:
a−n=1/an
| 🔹 Real-Life Application 🌍 |
Negative exponents are used in:
- Scientific notation for small numbers:
2.5×10−3=0.0025 - Physics and Chemistry to represent very small quantities like charge, mass, or wavelength.
| 🔹 Quick Tip 💡 |
Always remember:
- Negative exponents don’t make the value negative,
- they just flip the fraction!
| 🧩 Practice Problems |
- 3−2=?
- 1/4−3=?
- (52)−1=?
- 2−4×23=?
- (1/2)−2=?
Learn with an example
Write the expression as a fraction with a positive exponent. Do not evaluate the expression.
9-2
The base has a negative exponent, –2. You can rewrite the expression as a fraction with a numerator of 1 and a positive exponent, 2, in the denominator.
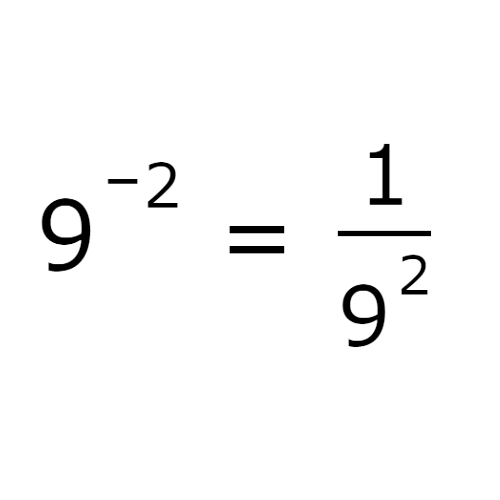
Write the expression as a whole number with a negative exponent. Do not evaluate the expression.
1/73
There is a positive exponent, 3, in the denominator. You can rewrite the expression with an exponent of –3 instead.
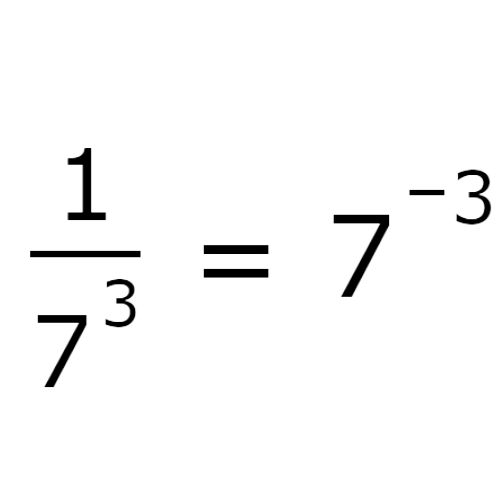
Evaluate. Write your answer as a fraction or whole number without exponents.
3–3 =

Let’s practice!🖊️

