Understanding negative exponents
Key Notes :
📘 Understanding Negative Exponents
| What is an exponent? |
An exponent tells us how many times a number (base) is multiplied by itself.
Example:
34=3×3×3×3=81
| What is a negative exponent? |
A negative exponent means that the number is reciprocal (1 divided by the number with a positive exponent).
Rule:
a−n=1/an(where a≠0)
Example:
- 2−3=1/23=1/8
- 5−2=1/52=1/25
| Why do negative exponents work? |
- Exponents follow the division rule:
am÷an=am−n
- If m<n, the exponent becomes negative:
a2÷a5=a2−5=a−3=1/a3
| Properties of Negative Exponents |
| Property | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Reciprocal Rule | a−n=1/an | 3−2=1/9 |
| Product Rule | a−m⋅a−n=a−(m+n) | 2−2⋅2−3=2−5=1/32 |
| Quotient Rule | a−m/a−n=a-(m−n) =an−m | 2−3/2−5=22=4 |
| Power Rule | (a−m)n=a−mn | (3−2)3=3−6=1/729 |
| Negative Exponents with Fractions |
- If the base is a fraction:
(a/b)−n=(b/a)n
Example:
(2/3)−2=(3/2)2=9/4
| Quick Tips ✅ |
- A negative exponent flips the base (reciprocal) and makes the exponent positive.
- a0=1 for any a≠0.
- Always write your final answer as a positive exponent when possible.
Learn with an example
Write the expression as a fraction with a positive exponent. Do not evaluate the expression.
9-2
The base has a negative exponent, –2. You can rewrite the expression as a fraction with a numerator of 1 and a positive exponent, 2, in the denominator.
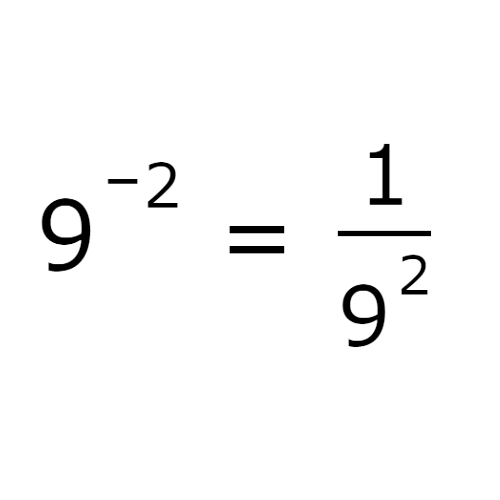
Write the expression as a whole number with a negative exponent. Do not evaluate the expression.
1/73
There is a positive exponent, 3, in the denominator. You can rewrite the expression with an exponent of –3 instead.
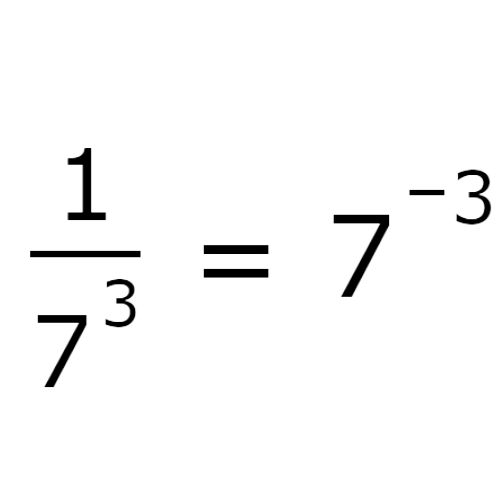
Write the expression as a fraction with a positive exponent. Do not evaluate the expression.
5–3
The base has a negative exponent, –3. You can rewrite the expression as a fraction with a numerator of 1 and a positive exponent, 3, in the denominator.
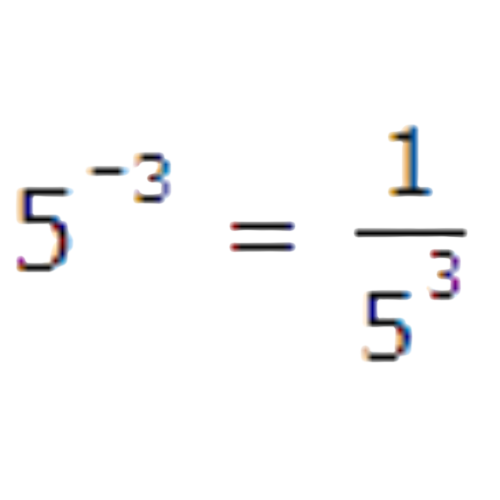
Let’s practice!🖊️

